Signs and Symptoms
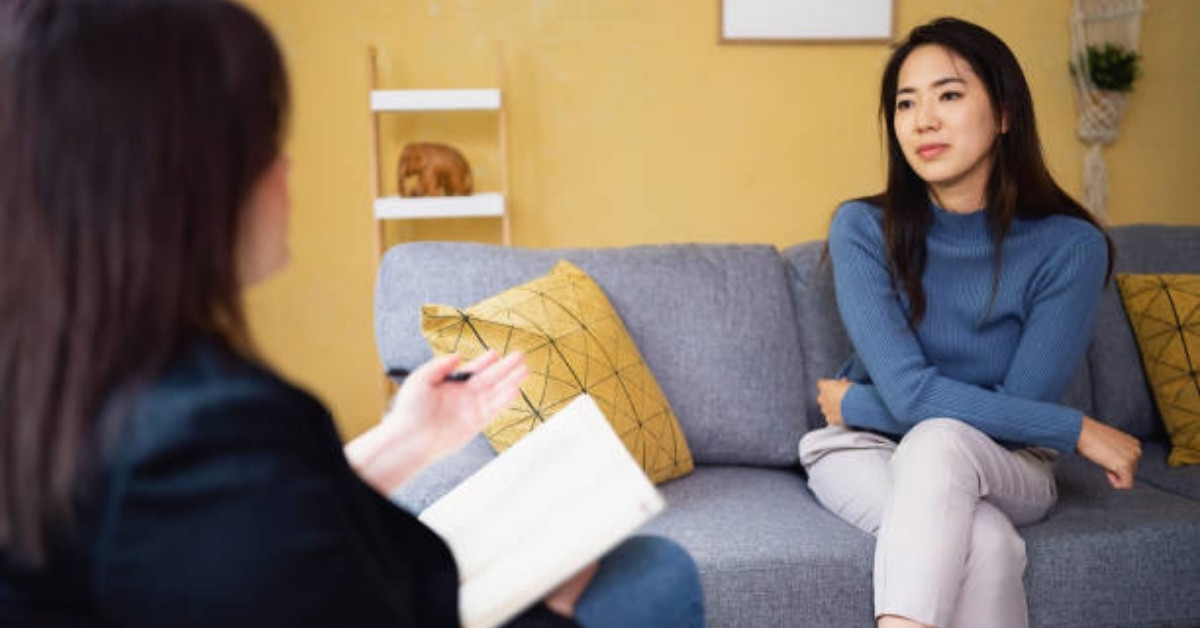
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of mental health issues is crucial in determining when is it time to seek mental health treatment. Many individuals may not be aware of the indicators that signal a need for help.
Recognizing Signs of Mental Health Issues
Common signs of mental health challenges can vary widely among individuals. These signs may manifest emotionally, physically, or behaviorally. Below is a table outlining some common symptoms and their potential descriptions.
| Sign/Symptom | Description |
| Persistent Sadness | Feeling sad or hopeless most days |
| Excessive Worry | Uncontrollable anxiety about daily tasks |
| Mood Swings | Rapid changes in mood and emotions |
| Social Withdrawal | Avoiding social interactions |
| Changes in Sleep Patterns | Insomnia or excessive sleeping |
| Appetite Changes | Significant weight loss or gain |
Awareness of these symptoms can help individuals recognize when they or someone they know may be struggling.
Understanding the Impact on Daily Life
Mental health issues can significantly affect an individual’s daily functioning and quality of life. These impacts can vary from mild disturbances to severe challenges that complicate everyday activities. The following table highlights different areas of life that may be affected by mental health problems.
| Area of Life | Potential Impact |
| Work Performance | Decreased productivity and focus |
| Relationships | Strained connections with family and friends |
| Physical Health | Increased fatigue and susceptibility to illness |
| Daily Activities | Difficulty in completing routine tasks |
Understanding how mental health issues can disrupt daily life emphasizes the importance of seeking help when needed. Observing these signs and impacts aids in recognizing critical moments that indicate when it is time to pursue mental health treatment.
When to Seek Help
Recognizing the right time to seek mental health treatment is essential for overall well-being. There are several key indicators that suggest it may be time to reach out for professional assistance.
Persistence of Symptoms
If symptoms of mental distress remain constant or worsen over time, it may indicate the need for treatment. Common symptoms can vary widely and may include feelings of sadness, anxiety, or emotional numbness.
| Symptom Type | Frequency & Duration |
| Sadness | Persistent for more than two weeks |
| Anxiety | Daily feelings of worry or panic that last for weeks |
| Mood Swings | Occurring several times a month without relief |
| Irritability | Constant irritability affecting daily life |
Interference with Functioning
When mental health symptoms begin to interfere with daily activities and responsibilities, it is crucial to consider seeking help. This can manifest in numerous ways, such as difficulty concentrating, maintaining relationships, or performing at work or school.
| Area of Impact | Description |
| Work | Poor job performance, missing deadlines, frequent absences |
| School | Declining grades, lack of participation, inability to complete assignments |
| Relationships | Conflicts with friends and family, social withdrawal |
| Daily Activities | Neglecting self-care, disinterest in hobbies |
Safety Concerns
Safety concerns are serious indicators that immediate help may be necessary. This includes any thoughts, plans, or actions related to self-harm or harm to others. If someone is experiencing these thoughts, it is important to seek professional intervention right away.
| Concern Type | Indicator |
| Self-Harm | Thoughts of self-inflicted harm or suicide |
| Suicidal Ideation | Planning or having a desire to end one’s life |
| Harm to Others | Having thoughts of harming others or committing violence |
Recognizing these signs and symptoms can empower individuals to take the necessary steps towards seeking help and improving their mental health.
Types of Mental Health Professionals
When considering mental health treatment, it is essential to understand the different types of professionals who can provide support and care. Each type of mental health provider has unique qualifications and areas of focus, making it important to choose the right one based on individual needs.
Psychiatrists
Psychiatrists are medical doctors who specialize in mental health. They can diagnose and treat various mental health disorders. Psychiatrists are able to prescribe medication, which is a significant distinction from other mental health professionals. Their medical training allows them to understand the biological aspects of mental health conditions.
| Qualification | Role |
| Medical Doctor (MD or DO) | Can prescribe medication |
| Residency in Psychiatry | Extensive training in diagnosing and treating mental illnesses |
Psychologists
Psychologists hold advanced degrees in psychology but are not medical doctors. They focus on therapy and counseling, using various techniques to help individuals overcome mental health issues. Psychologists conduct assessments to understand clients’ needs and can provide therapy based on scientific principles and psychological research.
| Qualification | Role |
| Doctorate in Psychology (PhD or PsyD) | Provides psychological assessments and therapy |
| Licensed by State | Must have state licensure to practice |
Counselors
Counselors are trained professionals who offer guidance and support for mental health issues. They typically hold a master’s degree in counseling or a related field. Counselors use talk therapy and other techniques to help individuals cope with life challenges, stress, and emotional difficulties. They may specialize in specific areas, such as school counseling, marriage and family therapy, or substance abuse counseling.
| Qualification | Role |
| Master’s Degree in Counseling | Provides talk therapy and support |
| May have Specific Certifications | Specializations in various areas of counseling |
Understanding the various types of mental health professionals can help individuals determine who to approach when considering if it is time to seek mental health treatment. Each type plays a unique role in providing care and support for mental well-being.
Treatment Options
When someone is considering when it is time to seek mental health treatment, various options are available. The most common treatment modalities include therapy, medication, and support groups. Each of these options serves different needs and can be effective depending on individual circumstances.
Therapy
Therapy, also known as psychotherapy or counseling, involves talking with a trained mental health professional. This option aims to help individuals understand their feelings, thoughts, and behaviors in a safe and confidential environment. Types of therapy can include:
| Type of Therapy | Description |
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. |
| Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) | Combines cognitive-behavioral techniques with mindfulness strategies. |
| Psychodynamic Therapy | Explores unconscious thoughts and feelings that influence behavior. |
| Group Therapy | Involves a small group of people who share similar experiences discussing their challenges. |
Medication
Medication can be an essential component of mental health treatment. It typically includes the use of psychiatric medications prescribed by a psychiatrist or primary care physician. Various categories of medications exist, each serving different purposes:
| Type of Medication | Purpose |
| Antidepressants | Often used to treat depression and anxiety disorders. |
| Antipsychotics | Used for conditions like schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. |
| Mood Stabilizers | Help manage mood swings, especially in bipolar disorder. |
| Anti-anxiety Medications | Designed to reduce symptoms of anxiety and panic. |
Choosing medication should involve careful consideration, as different individuals may respond differently to the same medication.
Support Groups
Support groups provide a platform for individuals dealing with similar issues to share experiences and offer mutual support. They are often led by a facilitator and can be beneficial in reducing feelings of isolation. Support groups may concentrate on specific issues, such as:
| Type of Support Group | Focus |
| General Mental Health | Open discussion for all mental health issues. |
| Depression Support Groups | Focused on experiences related to depression. |
| Anxiety Disorder Groups | For individuals experiencing anxiety-related challenges. |
| Grief Support Groups | For those coping with loss and bereavement. |
Participating in a support group can help individuals feel understood and encourage them to seek further treatment if necessary. Each of these treatment options—therapy, medication, and support groups—offers unique benefits and can be adapted to fit individual needs and circumstances.
How to Find Help
Navigating mental health issues can be challenging. When considering when it is time to seek mental health treatment, there are several useful resources available.
Primary Care Physicians
Primary care physicians play a crucial role in mental health care. They can assess symptoms, provide initial support, and refer individuals to specialized mental health professionals. A primary physician can also evaluate any physical health conditions that might be contributing to mental health symptoms.
| Services Offered by Primary Care Physicians |
| Initial assessment of mental health symptoms |
| Referrals to mental health specialists |
| Medication management |
| Coordination of care for physical and mental health |
Mental Health Hotlines
Mental health hotlines offer immediate support and guidance for individuals in crisis or those seeking answers. These hotlines provide access to trained professionals who can listen, provide resources, and guide individuals toward appropriate help.
| Hotlines and Their Purposes | | — | — | | National Suicide Prevention Lifeline | 24/7 support for individuals in crisis or emotional distress | | Crisis Text Line | Text-based support for those who prefer written communication | | Local mental health hotlines | Often available for specific communities or regions |
Online Resources
The internet is a valuable tool for finding information and support regarding mental health. Various online resources can provide educational material, self-help strategies, and directories to locate mental health professionals.
| Types of Online Resources |
| Educational Websites |
| Support Forums |
| Professional Directories |
By utilizing these resources, individuals can take proactive steps toward improving their mental wellbeing and deciding when it is time to seek mental health treatment.
Stigma and Barriers
Seeking mental health treatment can be challenging due to societal stigma and various barriers individuals may encounter. Understanding and addressing these factors is crucial for encouraging effective mental health care.
Overcoming Stigma
Stigma surrounding mental health often prevents individuals from seeking help. Negative attitudes and beliefs about mental illness create a culture of shame and misunderstanding. Educating the public about mental health issues can help combat these perceptions.
| Factor | Description |
| Public Awareness | Increased knowledge can reduce misconceptions. |
| Personal Stories | Sharing experiences can humanize mental health issues. |
| Supportive Communities | Encouraging open discussions fosters a safe environment to seek help. |
Empathy and understanding from friends and family can also play a key role in reducing stigma. A supportive network encourages individuals to acknowledge their struggles and reach out for necessary treatment.
Addressing Barriers to Seeking Help
There are several barriers that individuals may face when considering mental health treatment. These include financial constraints, lack of access to services, and limited knowledge of where to seek help.
| Barrier | Description |
| Financial Issues | Lack of insurance or high costs can prevent access to care. |
| Availability of Services | Shortage of mental health professionals in certain areas limits options. |
| Awareness of Resources | Many individuals may not know where to find help. |
Solutions to these barriers should include awareness campaigns, increased funding for mental health services, and providing information about available resources. Creating more accessible and affordable treatment options can significantly enhance individuals’ ability to seek help.
Sources
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/adult-health/in-depth/mental-health
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/knowing-when-to-seek-treatment
https://jedfoundation.org/mental-health-warning-signs-and-when-to-ask-for-help